Pneumonia is a common yet potentially serious respiratory infection that affects millions of people worldwide every year. It can strike anyone, from infants to the elderly, and its severity can range from mild to life-threatening. Understanding pneumonia—its symptoms, causes, treatment options, and prevention strategies—is crucial for protecting yourself and your loved ones. In this article, we’ll break down everything you need to know about pneumonia in a clear, engaging, and easy-to-understand way.
What Is Pneumonia?
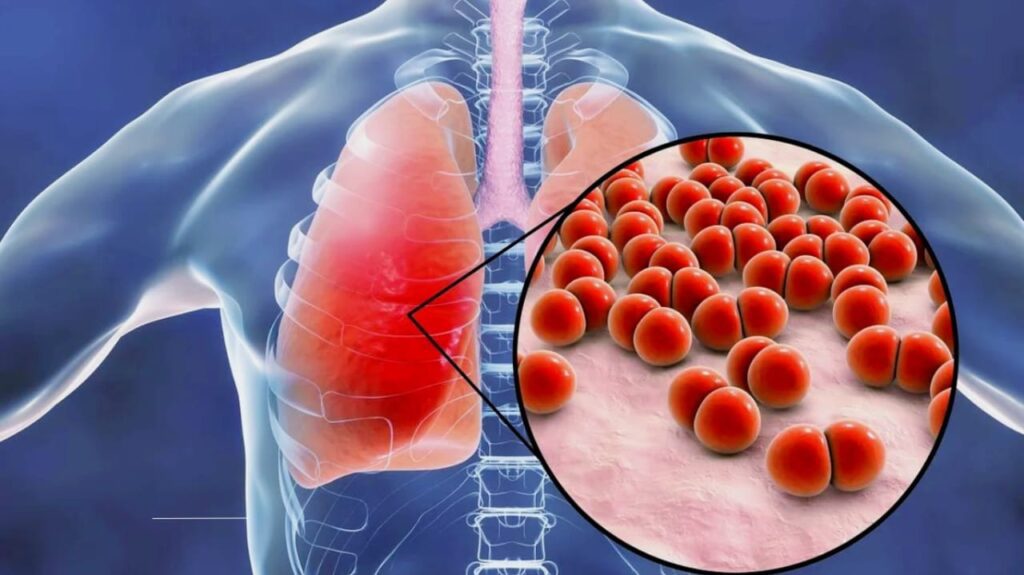
Pneumonia is an infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs. These air sacs, called alveoli, can fill with fluid or pus, making it difficult to breathe and causing symptoms like coughing, fever, and chest pain. While pneumonia can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi, bacterial pneumonia is the most common type in adults.
The infection can affect people of all ages, but certain groups are at higher risk, including young children, older adults, and individuals with weakened immune systems or chronic health conditions like asthma, diabetes, or heart disease. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), pneumonia is a leading cause of death among children under five globally, highlighting the importance of awareness and early intervention.
Symptoms of Pneumonia
Pneumonia symptoms can vary depending on the cause of the infection, the age of the patient, and their overall health. However, some common symptoms include:
- Cough: Often producing phlegm (mucus) that may be green, yellow, or even bloody.
- Fever: High fever with sweating and chills is a hallmark symptom.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing, especially during physical activity.
- Chest Pain: Sharp or stabbing pain that worsens when coughing or breathing deeply.
- Fatigue: Feeling unusually tired or weak, even after minimal exertion.
- Confusion: Particularly in older adults, pneumonia can cause mental confusion or delirium.
In infants and young children, symptoms may be less specific and include irritability, difficulty feeding, or a bluish tint to the lips and nails due to lack of oxygen.
It’s important to note that some cases of pneumonia, especially viral pneumonia or “walking pneumonia,” may present with milder symptoms that resemble a cold or flu. This can make it harder to diagnose without medical evaluation.
Causes of Pneumonia
Pneumonia can be caused by a variety of pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Here’s a breakdown of the most common causes:
- Bacterial Pneumonia:
- The most common cause is Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus).
- Other bacteria, such as Haemophilus influenzae and Legionella pneumophila, can also cause pneumonia.
- Bacterial pneumonia often occurs after a cold or flu, when the immune system is weakened.
- Viral Pneumonia:
- Viruses like influenza (flu), respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and SARS-CoV-2 (the virus that causes COVID-19) are common culprits.
- Viral pneumonia is typically less severe than bacterial pneumonia but can still be dangerous, especially in high-risk groups.
- Fungal Pneumonia:
- Fungi like Pneumocystis jirovecii can cause pneumonia, particularly in individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS.
- Fungal pneumonia is less common but can be severe if not treated promptly.
- Aspiration Pneumonia:
- This occurs when food, liquids, or vomit are inhaled into the lungs, leading to infection.
- It’s more common in people with swallowing difficulties, such as those recovering from stroke or under the influence of alcohol or drugs.
Treatment Options for Pneumonia
The treatment for pneumonia depends on the cause, severity, and overall health of the patient. Here’s an overview of the most common treatment approaches:
- Antibiotics:
- Bacterial pneumonia is typically treated with antibiotics like amoxicillin, azithromycin, or doxycycline.
- It’s crucial to complete the full course of antibiotics, even if symptoms improve, to prevent antibiotic resistance.
- Antiviral Medications:
- Viral pneumonia may be treated with antiviral drugs like oseltamivir (Tamiflu) for influenza or remdesivir for COVID-19.
- However, most viral cases are managed with supportive care, as antibiotics are ineffective against viruses.
- Antifungal Medications:
- Fungal pneumonia is treated with antifungal drugs like fluconazole or amphotericin B.
- Supportive Care:
- Rest, hydration, and over-the-counter medications like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help manage symptoms like fever and pain.
- In severe cases, hospitalization may be required for oxygen therapy, intravenous fluids, or mechanical ventilation.
- Preventing Complications:
- Vaccines, such as the pneumococcal vaccine and flu shot, can reduce the risk of developing pneumonia.
- Early diagnosis and treatment are key to preventing complications like sepsis or lung abscesses.
Prevention Tips for Pneumonia
Preventing pneumonia is often easier than treating it. Here are some practical tips to reduce your risk:
- Get Vaccinated:
- The pneumococcal vaccine protects against the most common bacterial cause of pneumonia.
- The flu vaccine can prevent influenza, which is a common precursor to pneumonia.
- Practice Good Hygiene:
- Wash your hands regularly with soap and water, especially before eating or touching your face.
- Use hand sanitizer when soap and water aren’t available.
- Avoid Smoking:
- Smoking damages the lungs and weakens the immune system, making you more susceptible to respiratory infections.
- Strengthen Your Immune System:
- Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Exercise regularly, get enough sleep, and manage stress to keep your immune system strong.
- Stay Away from Sick People:
- Avoid close contact with individuals who have colds, flu, or other respiratory infections.
- Practice Respiratory Etiquette:
- Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your elbow when coughing or sneezing.
- Dispose of tissues properly and wash your hands immediately.
- Manage Chronic Conditions:
- If you have asthma, diabetes, or heart disease, work with your healthcare provider to keep these conditions under control.
The Role of Lifestyle and Environment
Your lifestyle and environment can also play a significant role in your risk of developing pneumonia. For example:
- Air Pollution: Exposure to high levels of air pollution can irritate the lungs and increase the risk of respiratory infections.
- Crowded Living Conditions: Living in close quarters with others, such as in dormitories or nursing homes, can facilitate the spread of germs.
- Travel: Traveling to areas with high rates of infectious diseases can increase your risk of exposure.
By making informed choices and taking proactive steps, you can significantly reduce your risk of pneumonia and its complications.
Expert Insights on Pneumonia
According to Dr. Jane Smith, a pulmonologist at the Mayo Clinic, “Early detection and treatment are critical when it comes to pneumonia. If you or a loved one experience symptoms like persistent cough, fever, or difficulty breathing, don’t wait—seek medical attention right away.”
Studies have shown that vaccination is one of the most effective ways to prevent pneumonia. A 2020 study published in The Lancet found that the pneumococcal vaccine reduced the risk of pneumonia in older adults by 45%.
Case Study: A Real-Life Example
Consider the case of John, a 65-year-old man with diabetes. John developed a persistent cough and fever after recovering from the flu. Initially, he dismissed his symptoms as a lingering cold. However, when his condition worsened, he visited his doctor and was diagnosed with bacterial pneumonia. Thanks to prompt treatment with antibiotics and supportive care, John made a full recovery. His story underscores the importance of not ignoring symptoms and seeking medical help early.
Final Thoughts
Pneumonia is a serious but preventable and treatable condition. By understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options, you can take steps to protect yourself and your loved ones. Remember, prevention is always better than cure—so prioritize vaccinations, good hygiene, and a healthy lifestyle to keep pneumonia at bay.
